The Persian Gulf, a body of water nestled between Iran, the Arabian Peninsula, and the broader Middle East, has long been a focal point of international attention. With its rich historical significance and geopolitical relevance, this waterway plays a crucial role in shaping the economy, security, and diplomacy of the countries surrounding it. Throughout history, the Persian Gulf has been a vital crossroads for trade, culture, and military strategy, influencing regional and global powers alike. Dr.Graphic will explore the historical, economic, and geopolitical importance of the Persian Gulf and its strategic role in the modern world.
Historical Significance
The Persian Gulf’s importance is not just a modern phenomenon; its history spans thousands of years. In ancient times, it was home to some of the world’s earliest civilizations, including the Sumerians, Babylonians, and Persians. These civilizations relied heavily on the Persian Gulf for their maritime trade routes, which facilitated the exchange of goods, ideas, and cultures. The Gulf served as a meeting point for various cultures, with ports such as Bahrain, Kuwait, and the southern coasts of Iran playing key roles in the international trade network. This extensive trade also led to the spread of technological innovations, such as the wheel and the sail, which transformed transportation and commerce.
The Gulf’s role as a trading hub continued throughout the Islamic Golden Age, with cities like Basra and Baghdad thriving as centers of learning, culture, and commerce. The region was an essential link in the Silk Road, connecting the Middle East to India, China, and Africa, making it a vital crossroads for the exchange of goods and ideas.
The rise of the Persian Empire further solidified the strategic importance of the Persian Gulf. With its access to the Indian Ocean, the Persian Empire expanded its trade and influence throughout Asia, Africa, and Europe. The region’s historical role as a center for maritime trade and military strategy has shaped its modern significance, making it a critical part of global geopolitics.
Economic Importance
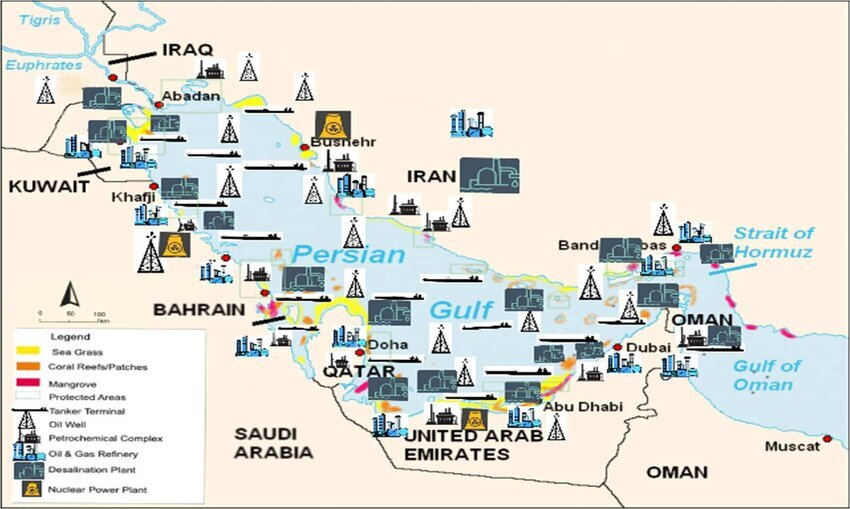
The Persian Gulf’s economic value cannot be overstated, as it contains some of the world’s largest reserves of oil and natural gas. The Gulf countries, particularly Saudi Arabia, Iran, and the UAE, hold a significant portion of the global energy supply, making the region a central player in global energy markets. The Gulf has been described as the “energy corridor” of the world, providing essential resources that power industries, economies, and households across the globe.
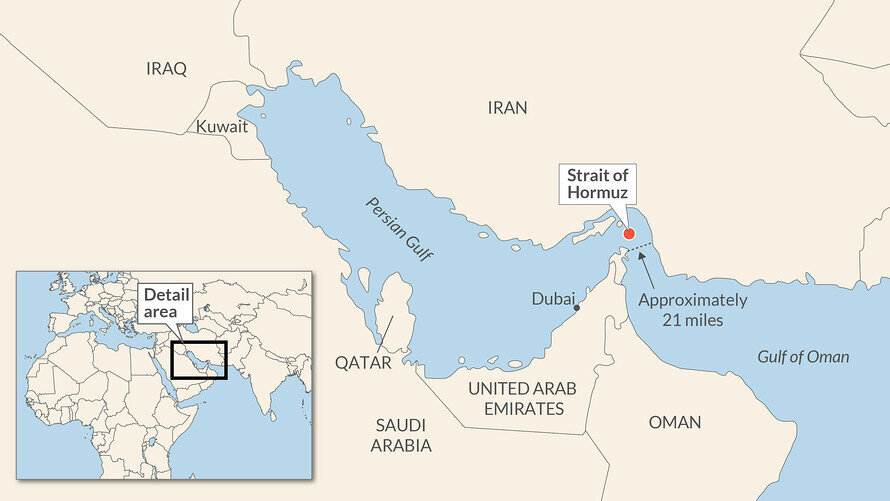
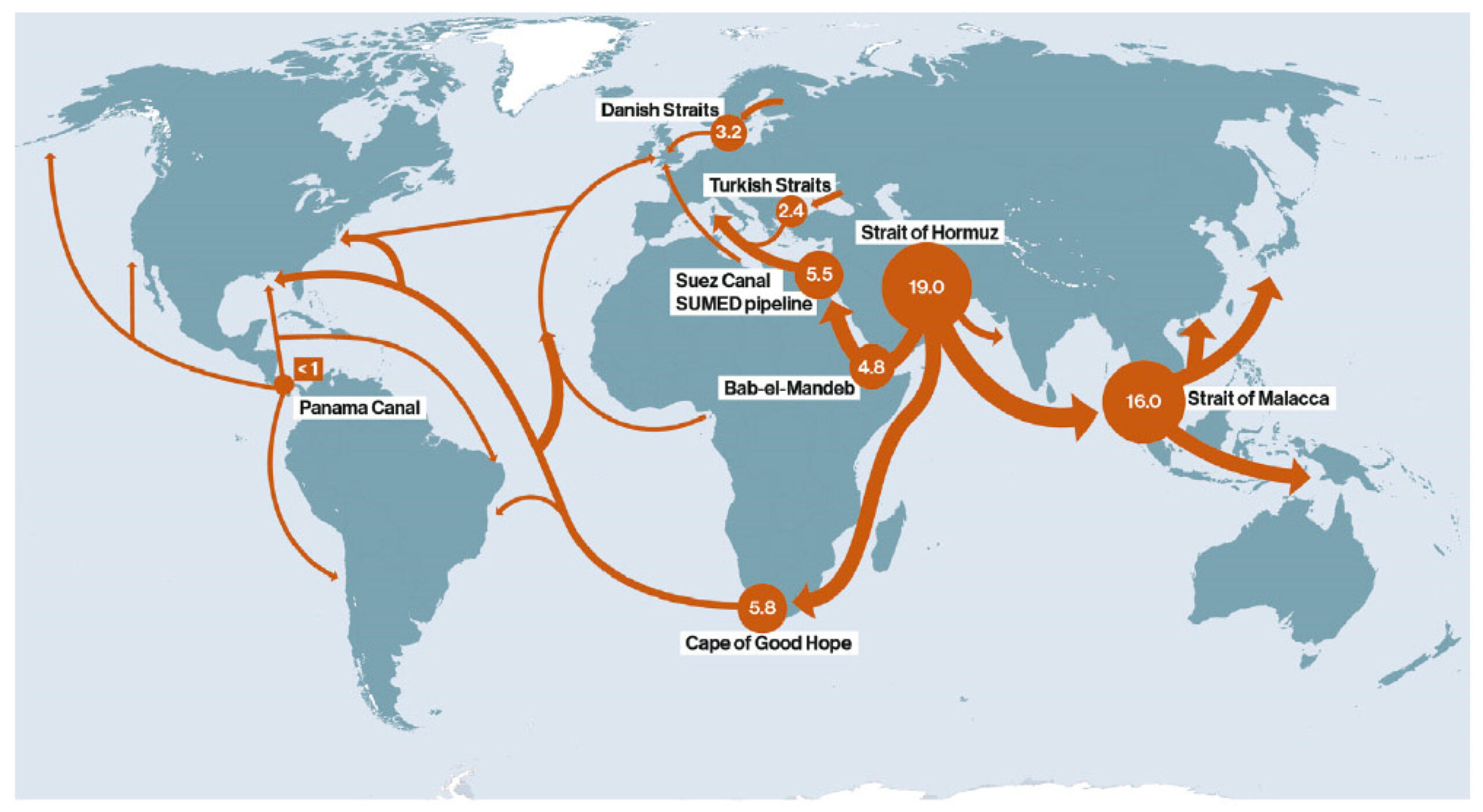
The Strait of Hormuz, a narrow waterway connecting the Persian Gulf to the Arabian Sea, is particularly important in terms of global energy supply. It is estimated that over 20% of the world’s oil passes through this strategic chokepoint daily. This makes the Persian Gulf an indispensable part of the global energy infrastructure. In addition to oil, the region is also a major producer of natural gas, with countries like Qatar and Iran holding some of the largest natural gas reserves in the world.
Beyond its energy resources, the Gulf is home to some of the busiest ports in the world, including Dubai’s Jebel Ali Port and Bahrain’s Khalifa Bin Salman Port. These ports are critical hubs for international trade, handling goods ranging from electronics and machinery to food and textiles. The Gulf’s location as a bridge between East and West has made it an essential link in the global supply chain, with goods flowing in and out of the region daily.
The economic importance of the Persian Gulf extends beyond its resources and ports. The region has seen rapid economic development in recent decades, driven by investments in infrastructure, tourism, and technology. Cities like Dubai and Doha have emerged as global financial and business centers, attracting international investment and talent. The Gulf countries have diversified their economies to reduce their dependence on oil, focusing on industries such as aviation, real estate, and finance.
Geopolitical Significance
The strategic location of the Persian Gulf has made it a geopolitical hotspot for centuries. Countries within the Gulf region, as well as external powers such as the United States, Russia, and China, have long recognized the area’s strategic value. The proximity of the Gulf to key global shipping routes, combined with its vast energy resources, makes it a region of immense importance to both regional and global powers.
The Persian Gulf has been the site of numerous conflicts, from the Iran-Iraq War to the Gulf War of the early 1990s, with the involvement of international coalitions. The Iran-Iraq War (1980–1988) was particularly devastating, as both countries sought to control the region’s oil resources and secure their influence over the Gulf. More recently, the Gulf has been a flashpoint for tensions between Iran and the United States, as well as other regional actors. The U.S. military has maintained a significant presence in the Gulf since the Gulf War, with military bases in Bahrain, Qatar, and the UAE.
The Persian Gulf is also a point of competition among regional powers, including Saudi Arabia, Iran, and the smaller Gulf states. These countries seek to exert influence over the region’s political and economic systems, often leading to diplomatic and military challenges. The rivalry between Saudi Arabia and Iran, in particular, has fueled tensions in the Gulf, as each country seeks to promote its own vision for the region’s future.
The presence of foreign military bases and naval forces in the Gulf further underscores the region’s strategic importance. The U.S. Navy’s 5th Fleet, based in Bahrain, patrols the waters of the Gulf, ensuring the free flow of oil and trade through the Strait of Hormuz. The geopolitical significance of the Persian Gulf is thus not limited to the countries within the region but extends to global powers with vested interests in maintaining stability and access to the region’s resources.
Environmental and Ecological Aspects
In addition to its historical, economic, and geopolitical significance, the Persian Gulf faces several environmental challenges. The Gulf’s ecosystem, which supports a rich diversity of marine life, is under pressure from industrial activities, oil extraction, and shipping. The region’s waters have been affected by oil spills, overfishing, and pollution, leading to a decline in marine biodiversity. Coral reefs, which are vital for supporting marine life, have also been damaged by human activities, including coastal development and the dredging of ports.
Efforts to address these environmental concerns have been made by Gulf countries, such as the establishment of marine protected areas and stricter regulations on oil drilling and waste disposal. However, balancing economic growth with environmental preservation remains a challenge. The rapid development of cities along the Gulf’s coastline has led to habitat destruction, while the growing demand for oil and gas continues to put pressure on the region’s natural resources.
The impact of climate change also poses a significant threat to the Persian Gulf. Rising temperatures, sea-level rise, and extreme weather events could further disrupt the delicate balance of the region’s ecosystem, leading to changes in marine species populations and coastal habitats.
Read more:
Conclusion
The Persian Gulf is far more than just a body of water; it is a region of immense historical, economic, and geopolitical importance. From its role in ancient trade to its current status as a key global energy hub, the Persian Gulf has shaped and will continue to shape global affairs. The region’s strategic location, rich resources, and complex geopolitical dynamics make it a focal point for both regional and global powers. As the Gulf faces new challenges, particularly in the areas of environmental sustainability and geopolitical tensions, its importance remains unchanged. The Persian Gulf will continue to be a key player on the global stage for years to come.
Resources: Wikipedia _ IRAN
How useful was this post?
Click on a star to rate it!
Average rating 4.8 / 5. Vote count: 4
No votes so far! Be the first to rate this post.