The Strait of Hormuz is one of the most strategically vital waterways in the world. Located between the Persian Gulf and the Gulf of Oman, this narrow passage connects the oil-rich countries of the Middle East to international markets. Iran, positioned along its northern border, plays a crucial role in its control and security. The strait is not just a political and economic hotspot; it also possesses breathtaking natural beauty that makes it an attractive destination for tourists and environmental enthusiasts. In this article, we will explore the geographical, economic, strategic, and touristic dimensions of the Strait of Hormuz, with a special focus on Iran’s role in the region. Stay with Dr.Graphic.
Geographical and Strategic Location
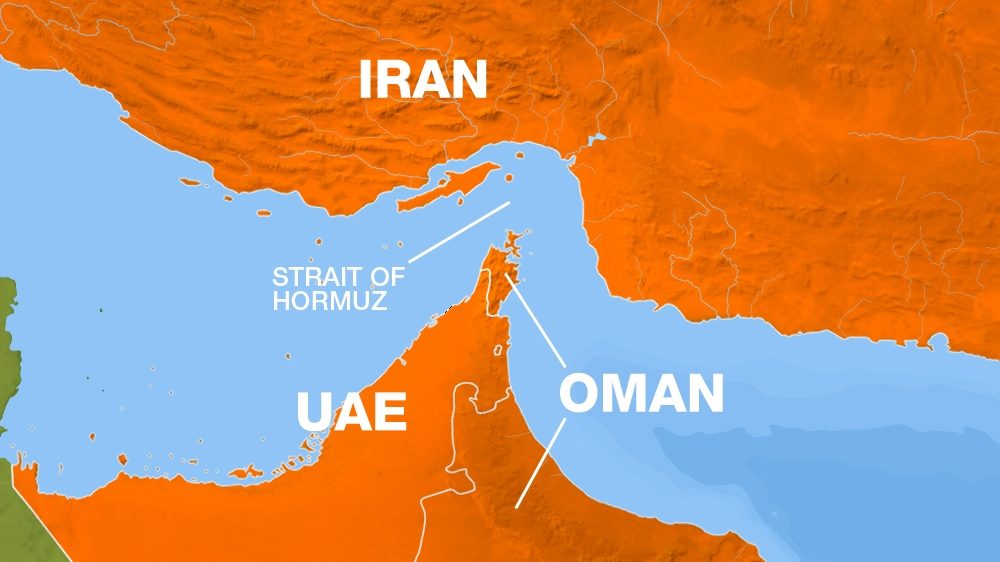
The Strait of Hormuz is situated between Iran to the north and Oman and the United Arab Emirates to the south. It is approximately 33 kilometers (21 miles) wide at its narrowest point, making it one of the most concentrated maritime chokepoints globally. The waterway serves as the sole sea passage from the Persian Gulf to the open ocean, giving it exceptional geopolitical value.
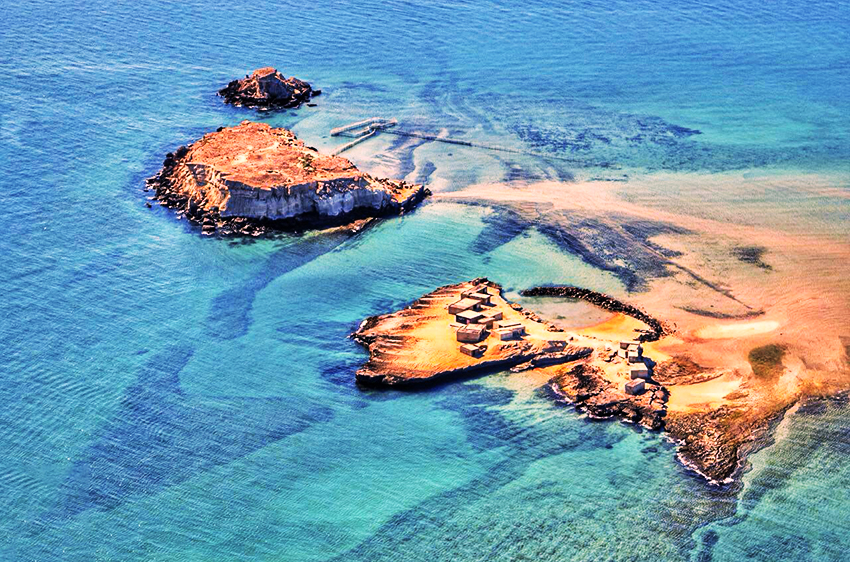
Several important Iranian islands lie in or near the strait, including Qeshm, Hormuz, Larak, and Hengam. These islands not only strengthen Iran’s maritime control but also contribute to the ecological and aesthetic richness of the area.
Economic Significance
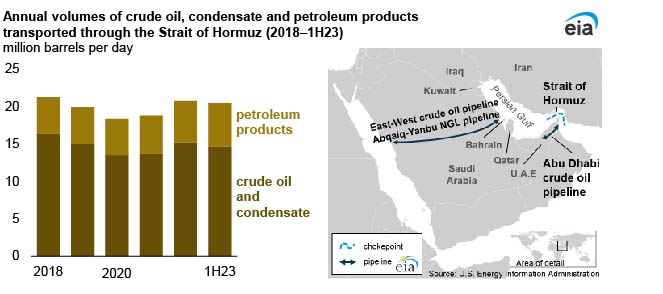
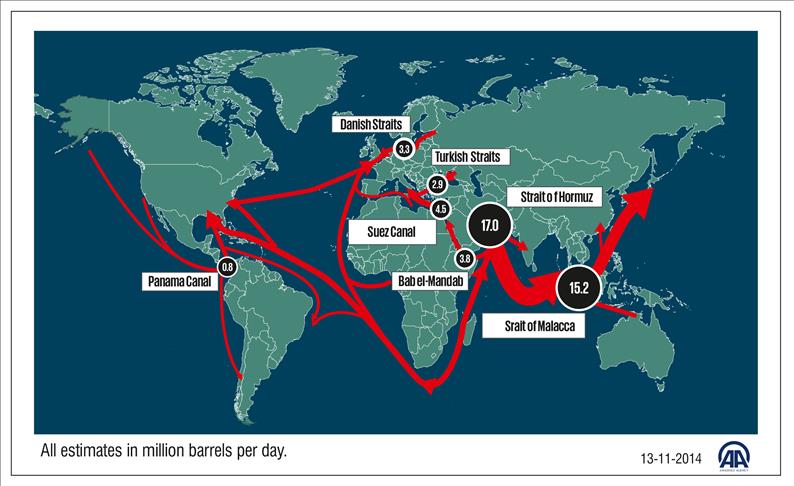
Around 20% of the world’s petroleum passes through the Strait of Hormuz, translating to over 17 million barrels per day. For major oil-producing countries such as Saudi Arabia, Iraq, Kuwait, the UAE, and Iran, the strait is the primary export route. Any disruption here could have immediate global consequences, driving up energy prices and threatening the global economy.
Iran benefits economically from its control and proximity to the strait. Bander Abbas, located on the northern coast, is one of Iran’s busiest commercial ports and serves as a gateway for import and export activities. Iran has also invested in Jask Port, east of the strait, as part of its strategy to diversify oil export routes and reduce reliance on the Persian Gulf.
Iran’s Role in the Strait
Iran’s geographic advantage gives it considerable influence over maritime traffic in the Strait of Hormuz. The Iranian military, particularly the Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps (IRGC) Navy, maintains a strong presence in the region. Through its control of key islands and naval bases, Iran is capable of monitoring or, if necessary, blocking passage through the strait.
Iran has often emphasized its role as a guardian of free navigation in the strait while simultaneously warning of retaliatory actions in response to sanctions or military threats. This dual approach reflects the nation’s broader geopolitical strategy: maintaining stability to ensure economic benefits while retaining leverage in international negotiations.
Security and Geopolitical Tensions
Over the decades, the Strait of Hormuz has been at the heart of numerous international conflicts. The Tanker War during the Iran-Iraq War in the 1980s saw oil tankers targeted in the strait, leading to military escorts and increased tensions. In more recent years, confrontations between Iranian forces and U.S. naval ships, as well as the seizure of oil tankers, have kept the region in the global spotlight.
The presence of foreign military forces—especially the United States, the United Kingdom, and other NATO allies—reflects the strait’s global importance. At the same time, it has heightened regional tensions, making the waterway both strategically vital and politically volatile.
Environmental and Maritime Challenges
Beyond geopolitics, the Strait of Hormuz faces several environmental concerns. The heavy flow of maritime traffic increases the risk of oil spills, marine pollution, and damage to fragile ecosystems. Additionally, climate change and rising sea temperatures are threatening the health of coral reefs and marine biodiversity.
Iran has made efforts to implement marine protection policies, particularly around the islands of Qeshm and Hormuz. These areas are rich in marine life and host unique geological features, such as salt domes and red sand beaches, that are increasingly targeted for conservation.
Natural Beauty of the Strait
In contrast to its political reputation, the Strait of Hormuz is also a region of remarkable natural beauty. The surrounding waters are crystal clear, often revealing colorful coral beds and diverse marine life such as dolphins, turtles, and rare fish species. The nearby islands of Qeshm and Hormuz are geologically unique and visually stunning.
- Hormuz Island, with its vibrant red soil known as “Golak,” attracts photographers and nature lovers.
- Qeshm Island boasts the Hara Mangroves, mysterious valleys, and caves, making it a destination for eco-tourism.
- Hengam Island offers dolphin-watching tours and serene beaches ideal for a peaceful getaway.
These areas are not only beautiful but also relatively untouched, offering a raw, authentic experience for nature tourists.
Tourism Potential and Attractions
Despite its security reputation, the Strait of Hormuz holds enormous tourism potential. In recent years, Iranian authorities have promoted the development of eco-tourism and cultural tourism in the region. Investment in boat tours, diving excursions, and island trekking is growing.
Local communities around the strait are also benefiting from tourism. On Hormuz Island, local art, handicrafts, and food have become major attractions, especially during Nowruz holidays, when thousands of Iranians visit the south. The unique combination of sea, sand, and local culture creates a tourism product unlike any other in the region.
The Iranian government’s effort to brand the region as a peaceful natural destination, while also maintaining necessary security protocols, is an essential part of a long-term sustainable tourism strategy.
Read more:
Getting to Know the Persian Gulf and its Strategic Importance
Conclusion
The Strait of Hormuz is far more than a geopolitical flashpoint; it is a complex and multifaceted region where strategic interests, economic needs, environmental concerns, and natural beauty intersect. For Iran, it is both a national security asset and a gateway to economic opportunity and tourism development.
By balancing its role as a regional power with sustainable practices and investment in tourism, Iran has the potential to turn this globally significant chokepoint into a symbol of both strength and serenity.
Resources: Wikipedia _ ALJAIRAH _ BBC
How useful was this post?
Click on a star to rate it!
Average rating 5 / 5. Vote count: 1
No votes so far! Be the first to rate this post.